Optimization in Deep Learning
Optimization is an essential concept in deep learning as the learning algorithms primarily affect the quality of the learned networks. This page introduces our group’s recent works on optimization, which are categorized by their topics.
Learning Algorithms for Deep Learning
Due to the non-convex property of the optimization problem in deep learning, it is important to understand its loss landscape while proposing new learning algorithms tailored to deep neural networks. We proposed several useful learning algorithms, including Madam and signSGD optimizers.
Madam Optimizer - Multiplicative Weight Update for Deep Learning (link)
We propose a multiplicative weight update method Madam - a multiplicative version of the Adam optimizer. We prove that multiplicative weight updates satisfy a descent lemma tailored to compositional functions. Our empirical results show that Madam can train state-of-the-art neural network architectures without learning rate tuning.
signSGD Optimizer: Sign-based Stochastic Gradient Descent (link)
We propose signSGD that updates the weights only using the sign of each minibatch stochastic gradient. Through theoretical analysis, we prove that signSGD matches the SGD-level convergence rate. On the practical side, we find that the momentum counterpart of signSGD is able to match the accuracy and convergence speed of Adam on deep Imagenet models.
Resource Constraint Optimization
Learning becomes computationally expensive with the increase of network sizes. This highlights the importance of resource constraint optimization, which aims to reduce resource consumption during training while preserving the quality of the solutions. We deigned effective learning algorithms for specific computational scenarios, such as distributed training and low-precision training.
LNS-Madam: Low-Precision Training in Logarithmic Number System using Multiplicative Weight Update (link)
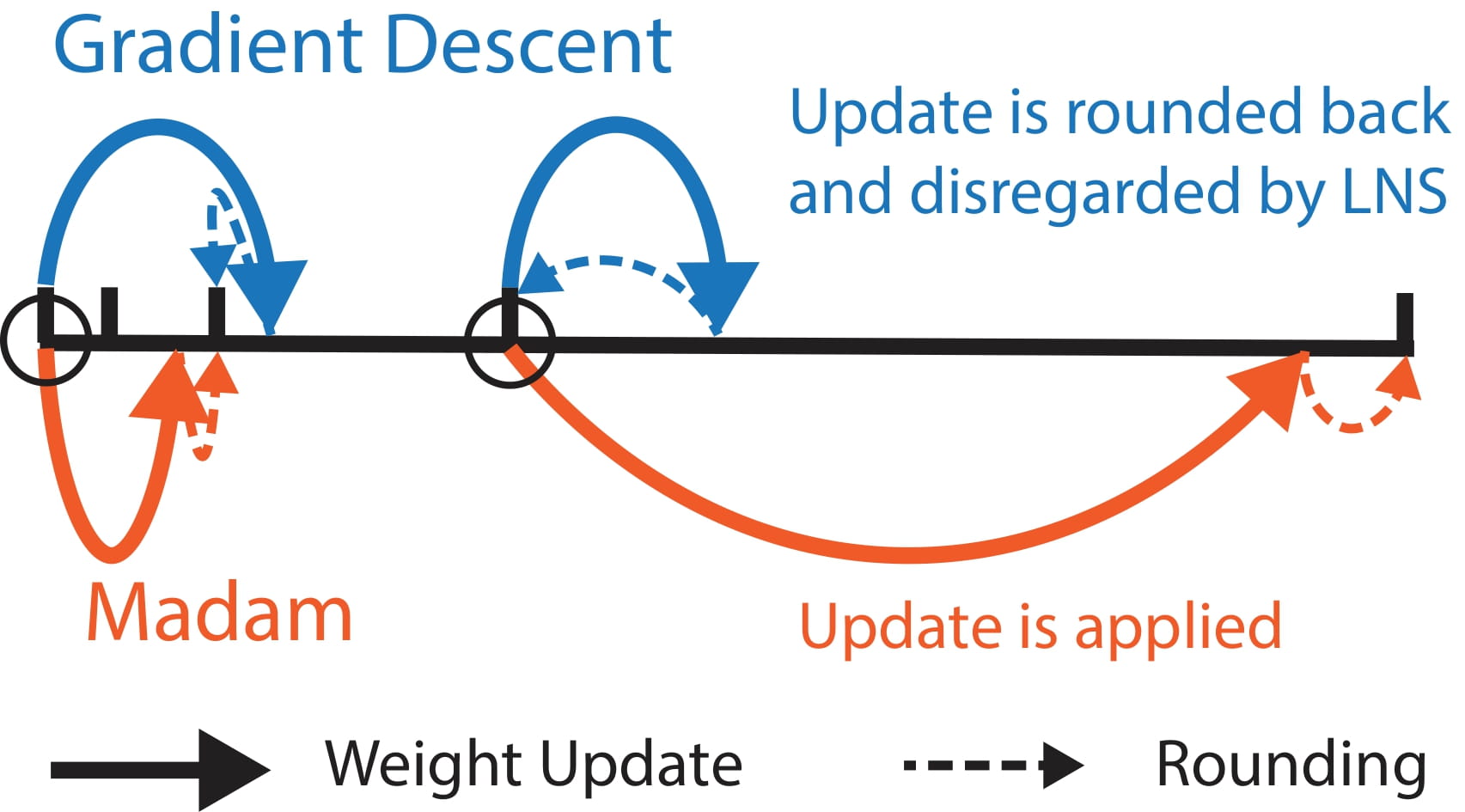
We develop a co-designed low-precision training framework LNS-Madam, in which we jointly design the logarithmic number system (LNS) and the multiplicative weight update algorithm Madam. We prove that Madam induces less quantization error as it directly updates the weights in a logarithmic representation. Thus, training with Madam leads to a stable convergence even if precision is strongly limited.
signSGD with Majority Vote: Distributed Learning using signSGD Algorithm (link)
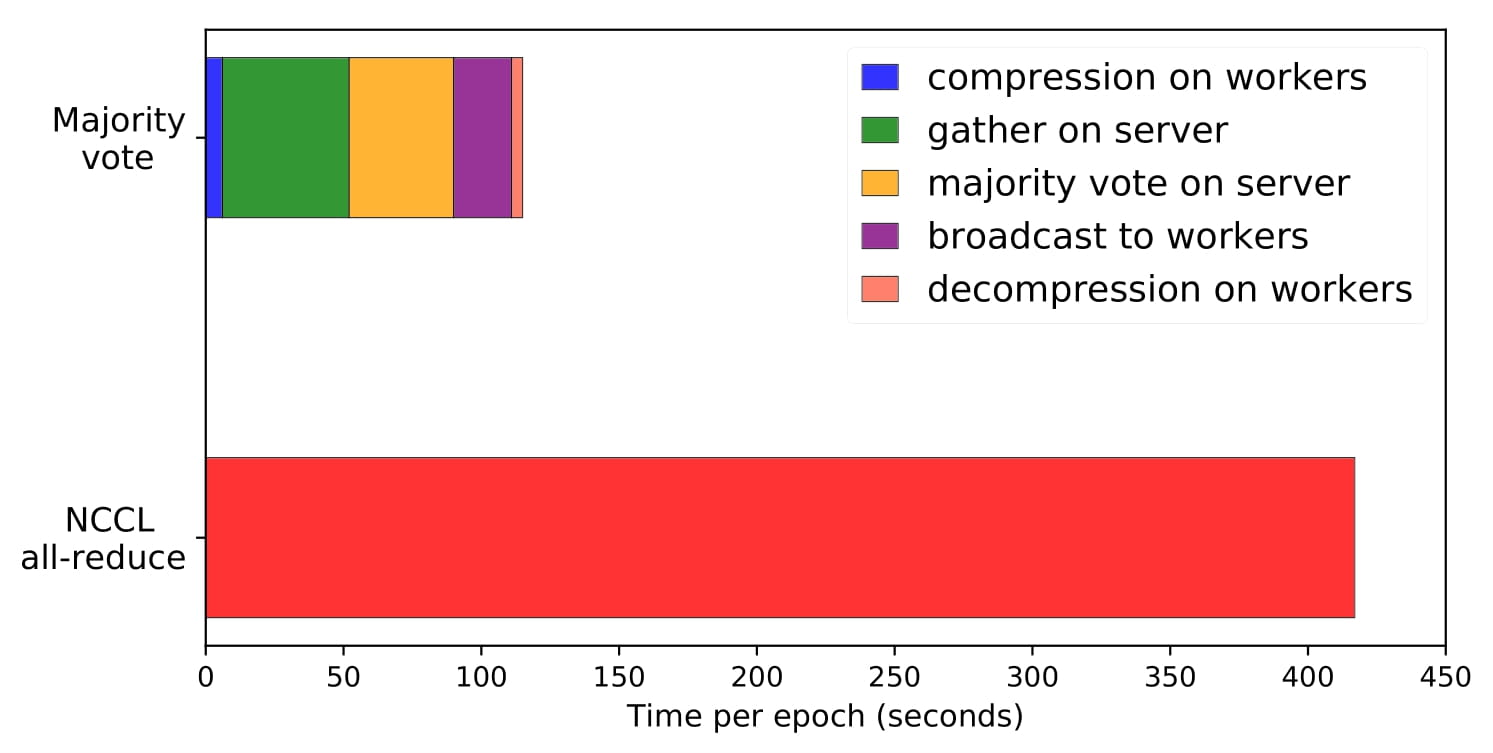
We propose signSGD with majority vote - a robust, communication-efficient learning algorithm for distributed learning. Workers transmit only the sign of their gradient vector to a server, and the overall update is decided by a majority vote. This algorithm uses 32× less communication per iteration than full-precision, distributed SGD. Benchmarking against the state-of-the-art collective communications library (NCCL), our framework leads to a 25% reduction in time for training resnet50 on Imagenet when using 15 AWS p3.2xlarge machines.
Multi-Agent Optimization
CGD Optimizer: Competitive Gradient Descent (link)
To be filled.
Competitive Gradient Descent for GAN Training (link)
To be filled.
Polymatrix Competitive Gradient Descent (link)
To be filled.
Policy Optimization
To be filled.
Competitive Policy Optimization (link)
To be filled.
Deep Bayesian Quadrature Policy Optimization (link)
To be filled.
Trust Region Policy Optimization of POMDPs (link)
To be filled.
Landscape Analysis
To be filled.
Efficient approaches for escaping higher order saddle points in non-convex optimization (link)
To be filled.